|
:::
 |
 |
 |
  |
|
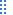
MRI |

|

|
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a test that provides pictures of organs and structures inside the body. It produces these images by using a magnetic field and pulses of radio wave energy. In many cases, MRI provides information that cannot be obtained from X-ray tests
For an MRI test, the area of the body being studied is positioned inside a strong magnetic field. The MRI can detect tumors, infection, and other types of tissue disease or damage. It can also help diagnose conditions that affect blood flow. Tissues and organs that contain water provide the most detailed MRI pictures, while bones and other hard materials in the body do not show up well on MRI pictures. For these reasons, MRI is most useful for detecting conditions that increase the amount of fluid in a tissue, such as inflammation, infection, tumors, and internal bleeding. Information from an MRI scan can be saved and stored on a computer for further study. Photographs or films of selected views can also be made.
In some cases a contrast material may be used during the MRI scan to enhance the images of certain structures. The contrast material may help evaluate blood flow, detect some types of tumors, and locate areas of inflammation. |

|
Why It Is Done? |

|

|
MRI is used to detect problems of the: |
- Head and brain (including the ears). MRI can help detect brain tumors, blood clots, a bulge in the wall of a blood vessel (aneurysm), bleeding in the brain, nerve fiber destruction caused by multiple sclerosis (MS), and other types of brain damage (such as damage caused by a stroke). MRI can also reveal problems of the eyes, the nerves leading from the eyes to the brain (optic nerves), the ears, and the nerves leading from the ears to the brain (auditory nerves). For more information, see the medical test Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Head.
- Chest (including the heart). MRI can be used to look at structures of the heart, such as the valves and coronary blood vessels. It can also detect damage to the heart or lungs (such as from tumors).
- Blood vessels. The use of MRI to look at blood vessels and the flow of blood through them is called magnetic resonance angiography (MRA). It can help detect problems of the arteries and veins, such as a bulge in the wall of an artery (aneurysm), blockage of a blood vessel (by fatty deposits or a blood clot), or a torn inner lining of a blood vessel (dissection). For more information, see the medical test Magnetic Resonance Angiography.
- Abdomen. MRI can detect problems of the organs and structures in the abdomen, such as tumors, bleeding, infection, and blockage. Malformations in structures, such as in the ureters, may also be detected by MRI.
- Bones and joints. MRI can help detect some problems of the bones, joints, and soft tissues of a joint (such as cartilage, ligaments, and tendons). Conditions that can be evaluated include arthritis, problems with the joint in the jaw (temporomandibular joint), bone marrow disorders, bone tumors, cartilage tears, worn-out cartilage, torn ligaments, or infection. MRI may also help diagnosis a bone fracture when X-ray results are inconclusive. MRI is done more commonly than other tests (such as arthrography) to evaluate certain bone and joint problems.
- Spine. MRI can be used to help diagnose conditions such as spinal stenosis, disc bulges, and spinal tumors. See Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Spine test.
|

|
How to Prepare |

|

|
Before the MRI test, tell your doctor if you: |
- " Have a pacemaker, artificial limb, any metal pins or metal fragments in your body (especially in the eyes), metal heart valves, metal clips in your brain, metal implants in your ear, tattooed eyeliner, or any other implanted or prosthetic medical device (such as a drug infusion pump). Also, tell your doctor if you have worked around metal or if you have recently had surgery on a blood vessel. In some cases you may not be able to have the MRI test done.
- Have an intrauterine device (IUD) in place. An IUD may prevent you from having the MRI test done.
- Are or might be pregnant.
- Become very nervous in confined spaces. You need to lie very still inside the MRI magnet, so you may need to have the test done with open MRI equipment that is not as confining as conventional MRI machines, or you may need medication to help you stay relaxed. For certain MRI studies (such as of the legs or lumbar spine), your body will be out of the confined space.
- " Have allergies of any kind (such as hay fever, hives, food or medication allergies, or allergic forms of asthma). The contrast material used for MRI does not contain iodine. If you have a known allergy to the contrast material used for MRI, tell your doctor before having another test. Sometimes the benefits of having this test may outweigh the risks. Other conditions (such as serious kidney problems and sickle cell anemia) may prevent you from having an MRI using contrast material
|

|
How It Is Done? |

|

|
An MRI test is usually done by a radiology technologist or MRI technologist. The resulting pictures are usually interpreted by a doctor who specializes in evaluating X-rays (radiologist). However, some other types of doctors (such as a neurologist, orthopedist, or vascular surgeon) can also interpret an MRI scan.
You will need to remove all metal objects (such as hearing aids, dentures, jewelry, watches, and hairpins) from your body because these objects may be attracted to the powerful magnet used for the test. If you have had an accident or you work around metal and there is a possibility that you have metal fragments in your head, eyes, skin, or spine, X-rays may be taken before the MRI to confirm the presence of metal and to determine whether you can have the test.
You will need to take off all or most of your clothes, depending on which area is examined (you may be allowed to keep on your underwear if it does not interfere with the test). You will be given a cloth or paper covering to use during the test. If you are allowed to keep some of your clothes on, you should empty your pockets of any coins and cards (such as credit cards or ATM cards) with scanner strips on them because the MRI magnet will erase the information encoded on the cards.
During the test you will lie on your back on a table that is part of the MRI scanner. Your head, chest, and arms may be secured with straps to help you remain still. The table will slide into the narrow tunnel that contains the magnet. Depending on the part of your body to be examined, your head, limbs (such as your legs), or your entire body will be moved into the center of the magnet. Some MRI machines (called open MRI) are now made so that the magnet does not completely surround the person being tested. Open MRI is less confining than a standard MRI scan.
Inside the scanner you will hear a fan and feel air moving. You may also hear tapping or thumping noises as the MRI scans are taken. It is very important to hold completely still while the scan is being done. Otherwise, repeat scans may be needed.
During the test, you will be probably alone in the scanner room. However, the technologist will watch you through an observation window, and you will be able to talk to him or her through an intercom.
If you are to be given contrast material, it will be injected (usually in your arm) over 1 to 2 minutes. Then additional MRI scans are done.
An MRI test usually takes 30 to 60 minutes, but because of delays that can occur, you should allow at least 2 hours for the test. |

|
How It Feels |

|
You will feel no discomfort from the magnetic field or radio waves used for the MRI test. However, the table you lie on may feel hard and the room may be chilly. You may become uncomfortable from lying in one position for a long time.
Some people feel discomfort or anxiety (claustrophobic) inside the MRI magnet. If this keeps you from lying still, you can be given medication (sedative) to help you relax. Open MRI machines are less confining than a standard MRI and may be helpful if you are claustrophobic. |

|
Risks |

|
There are no known harmful effects from the strong magnetic field used for MRI. However, the magnetic field is so powerful that it can send metal objects flying across the room. The magnet may affect pacemakers, artificial limbs, and other medical devices that contain iron. Also, there is a risk that metal objects coming near the magnet may become dangerous as they are pulled toward the magnet. The magnetic field will stop a watch that is within several yards of the magnet.
If metal fragments are in the eyes, MRI can cause damage to the retina. Iron pigments in tattooed eyeliner can cause eye irritation.There is slight risk of developing an allergic reaction if contrast material is used during the MRI scan. However, most reactions are mild and can be controlled using medication. |

|
Results |

|

|
The radiologist may discuss preliminary results of the MRI with you right after the test. Complete results are usually available in 1 to 2 days.
An MRI scan can sometimes detect a problem in a tissue or organ, even when the size and shape of the tissue or organ appear normal. However, because dense objects such as bone, calcifications, or kidney stones do not show up well on an MRI image, they are usually not studied using MRI.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) |
Normal |
The organs, blood vessels, bones, and joints are normal in size, shape, and location. |
| No abnormal growths (such as tumors) are seen. |
| No bleeding, abnormal collections of fluid, blockage in the flow of blood, or bulges in the blood vessels (aneurysms) are seen. |
| No signs of inflammation or infection are seen. |
Abnormal |
An organ may be abnormally large or small, or it may be damaged. |
| Abnormal growths (such as tumors) may be seen. Signs of infection in an organ or other structure in the body may be seen. |
| An abnormal collection of fluid (indicating a problem such as internal bleeding or infection) may be seen. Fluid in the lungs or around the heart may be seen. |
| A bulge in the wall of a blood vessel (aneurysm) may be seen. Blockage in or narrowing of a blood vessel may be seen. |
| Blockage may be seen in the intestines or other passages in the body (such as in the bile ducts). |
| Damage to joints, ligaments, or cartilage may be seen. Bones may show signs of infection, disease, or fracture. |
|

|
What Affects the Test ? |

|
Although the strong magnetic field used for an MRI does not appear to be harmful, an MRI test usually is not done for a pregnant woman. If a view of a pregnant woman's abdomen is needed, an ultrasound test may be done instead
Medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or cause problems during an MRI scan. Therefore, this test is often not done for a woman who has an intrauterine device (IUD) or for a person who has a pacemaker, certain types of artificial limbs, or a drug infusion pump in place.
The results of an MRI test may not be accurate if the person cannot remain still during the test
A person who is very overweight may not fit into the opening of some standard MRI machines. |
|
 |
|
 |